HSS Rolls (High-Speed Steel Rolls)
High-speed steel (HSS) rolls play a critical role in the operation of rolling mills, where they are used to shape and process metal at elevated temperatures. In rolling mills, metal is passed through a series of rolls that reduce its thickness and improve its properties. HSS rolls are ideal for this environment due to their excellent heat resistance, maintaining their hardness and strength even at the high temperatures typically encountered in hot rolling processes. These rolls are able to withstand the extreme stresses, abrasion, and wear that occur during the deformation of metals like steel, ensuring a smooth and consistent finish.

Technical Specifications:-
The technical specifications of high-speed steel (HSS) rolls used in hot rolling mills typically include a combination of alloy composition, hardness, heat resistance, and mechanical properties tailored to withstand the demanding conditions of metal processing. HSS rolls are generally made from alloys containing tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, vanadium, and carbon, with specific ratios that enhance the roll's ability to resist high temperatures and wear. These rolls are also designed to have excellent thermal shock resistance, allowing them to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking or deforming
Chemical Properties:-
Manufactured using high-alloy steel with elements such as tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), and cobalt (Co), HSS rolls offer excellent resistance to thermal fatigue, oxidation, and abrasive wear, making them ideal for finishing stands in hot rolling mills.
- Carbon (C): 1.50 / 2.20 – Enhances hardness and wear resistance by forming carbide phases.
- Chromium (Cr): 3.00 / 8.00 – Improves oxidation resistance, toughness, and hardenability.
- Molybdenum (Mo): 2.00 / 8.00 – Enhances high-temperature strength and resistance to softening.
- Vanadium (V): 2.00 / 9.00 – Forms fine vanadium carbides (VC) that increase wear resistance.
- Tungsten (W): 2.00 / 8.00 – Provides excellent red hardness and thermal fatigue resistance.
- Nickel (Ni): 0.00 / 1.50 – Improves toughness and impact strength.
- Silicon (Si): 0.31 / 1.00 – Enhances thermal fatigue resistance, helping the roll withstand the rapid temperature fluctuations commonly experienced in rolling mills.
- Manganese (Mn) : 0.40 / 1.20 – It acts as a deoxidizer during steelmaking and enhances the roll’s ability to form a uniform microstructure. Manganese also supports carbide formation, which contributes to better abrasion resistance.
- Phosphorus (P) : Typically below 0.030 – Phosphorus is kept at very low level. While it can slightly increase strength and hardness, its negative impacts outweigh the benefits. Phosphorus tends to make the steel brittle, reducing toughness and thermal fatigue resistance, which are critical for HSS roll performance under high-stress and high-temperature conditions. Excessive phosphorus can also lead to cracking and premature roll failure, so strict control is essential during production
- Sulfur (S) : Typically below 0.025 – sulfur can be beneficial in small amounts for improving machinability during roll manufacturing, its presence in service degrades critical properties such as toughness, thermal fatigue resistance, and hot strength. For this reason, sulfur content in HSS rolls is strictly controlled and minimized during production to ensure longer life, consistent performance, and safety in rolling mill operations.
Instructions for Using HSS Rolls in Rolling Mills
1. Proper Roll Handling
- Always handle HSS rolls with lifting belts, cradles, or clamps—never use chains directly on roll surfaces.
- Store rolls in clean, dry, and vibration-free areas to prevent corrosion and micro-cracking.
2. Surface Inspection Before Use
- Visually inspect roll surfaces and grooves for cracks, pits, or scale before mounting.
- Clean the roll surface thoroughly to remove dust, oil, or rust, especially from grooves.
3. Mounting & Alignment
- Ensure proper axial and radial alignment during mounting to avoid uneven wear or vibration.
- Use torque-controlled tightening to secure the rolls in chocks or holders.
4. Water Quality & Cooling
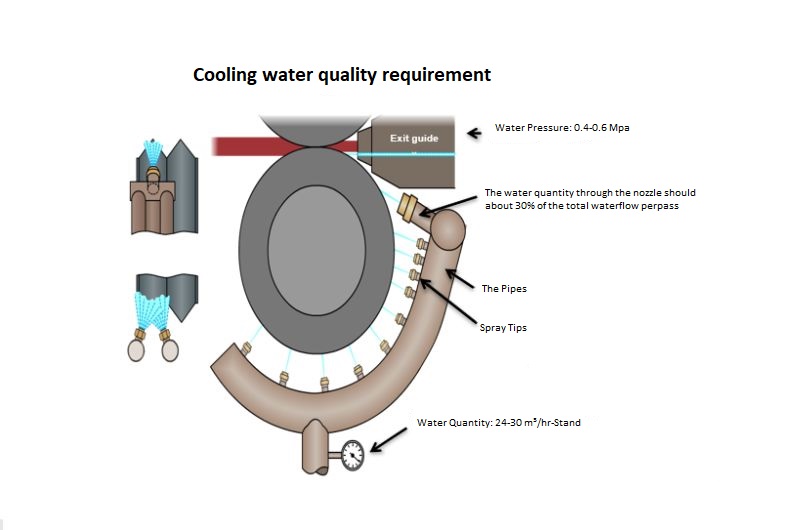
- Maintain consistent cooling during operation to avoid thermal cracking and extend groove life.
- Ensure direct, uniform cooling on rolling surface and grooves, especially in high-speed mills.
- Maintain water pressure at 0.4-0.6 MPa for effective performance.
- Use clean, filtered water (pH 7.2 to 8.0) with controlled pressure as told in above point and with discharge rate of 300-400 liters/min.
- Maintain TDS level range between 250-400 for optimal performance.
- Each HSS roll requires a C-Type stand nozzle for roll pulling and the diameter of nozzle should be 4-5 mm. The Gap that is to be maintained between nozzle to nozzle should be 20-24 mm to optimize cooling efficiency.
5. Rolling Parameters
- Avoid excessive loads beyond the roll’s rated hardness or toughness.
- Maintain consistent rolling speed, temperature, and reduction ratios to prevent surface damage.
- Monitor for vibration, chatter marks, or scoring, which may indicate improper mill settings.
6. Regular Groove Wear Monitoring
- Measure groove wear periodically to track roll life and determine regrinding schedules.
- Replace rolls or switch positions based on wear thresholds defined by mill specs.
7. Regrinding & Roll Shop Practices
- Use CNC grinding machines with appropriate wheels and coolant to maintain groove geometry and surface quality.
8. Roll Rotation or Exchange
- For multi-groove rolls, rotate grooves evenly in sequence to balance wear.
- Maintain a record of groove usage and performance to maximize roll lifespan.
9. Safety Measures
- Always wear PPE when handling or operating near rolls.
- Never operate the mill if abnormal roll behavior or noise is detected—shut down and inspect immediately.
